Peripheral Neuropathy and Foot Care Practices Among Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Attending a Tertiary Care Hospital: A Cross-sectional Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22502/jlmc.v10i2.473Keywords:
Diabetes mellitus, Foot care practices, Foot ulcers, Peripheral neuropathyAbstract
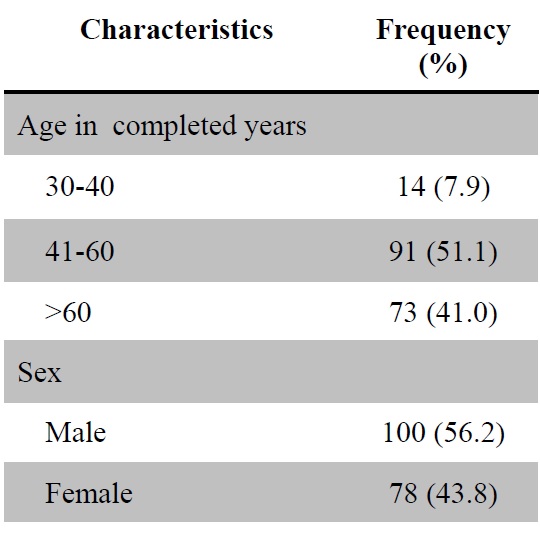
Introduction: Peripheral neuropathy is the most common microvascular complication of diabetes mellitus. Foot care is an important part of diabetes management. This study aimed to identify the prevalence of peripheral neuropathy and foot care practices among diabetic patients. Methods: A descriptive cross-sectional study was conducted on 178 patients diagnosed with diabetes mellitus and attending out-patient and in-patient departments of Internal Medicine at Kathmandu University Hospital, Dhulikhel. The participants were conveniently selected. Face-to-face interviews and a foot examination were used to collect data. The Michigan Neuropathy Screening Instrument and the Nottingham Assessment of Functional Foot Care were used to determine the prevalence of peripheral neuropathy and to assess foot care practices. Results: The prevalence of peripheral neuropathy was 41% among the participants, and it was associated with increasing age. The majority (75.8%) of the participants had good foot care practices. Male gender was significantly associated with good foot care practices [AOR = 5.973, 95% CI (2.037-17.515)], whereas past smokers [AOR = 0.296, 95% CI (0.111-0.791)] and not receiving diabetes education [AOR = 0.367, 95% CI (0.151-0.892)] were significantly associated with poor foot care practices. Conclusion: The prevalence of peripheral neuropathy was found to be high, and it was linked to an increased age group. The majority of the participants had good foot care practices. However, in comparison, females were found less likely to practice foot care than males.
Downloads
References
International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas [Internet]. Belgium: IDF, 2019. [Cited 2021 jan 7]. Available from: https://www.diabetesatlas.org/upload/resources/material/20200302_133351_IDFATLAS9e-final-web.pdf
Bodman MA, Varacallo M. Peripheral Diabetic Neuropathy [Internet]. Treasure Island: StatPearls Publishing, 2021. [cited 2021 Sep 8]. PMID: 28723038 Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK442009
American Diabetes Association. Peripheral Neuropathy [Internet]. American Diabetes Association, 2021 [cited 2021 Sep 8]. Available from: https://www.diabetes.org/diabetes/complications/neuropathy/peripheral-neuropathy
Pop-Busui R, Boulton AJM, Feldman EL, Bril V, Freeman R, Malik RA. Diabetic Neuropathy: A Position Statement by the American Diabetes Association. 2017;40(1):136-54. PMID: 27999003 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2337/dc16-2042
D’Souza M, Kulkarni V, Bhaskaran U, Ahmed H, Naimish H, Prakash A, et al. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy and its determinants among patients attending a tertiary health care centre in Mangalore. J Public Health Res. 2015;4(2):450. PMID: 26425491 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4081/jphr.2015.450
Rai ON, Mishra V, Chandra R, Saxena SK, Mangal BD. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy and its metabolic determinants in a north indian population. National Journal of Integrated Research in Medicine. 2016;7(2):1-4Available from: http://nicpd.ac.in/ojs-/index.php/njirm/article/view/1156
KC A, Kansakar A, Poudel A. Prevalence of complications in newly diagnosed diabetes mellitus visiting Nepal Medical College & Teaching hospital. Nepal Med Coll J. 2018;20(1-3):78-82. Available from: https://journal.nmcth.edu/journal_vol/5.
Shrestha HK, Katwal PC. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in T2DM Patient Presenting to Community Hospital in Nepal. Kathmandu Univ Med J (KUMJ). 2017;17(58):146-49. PMID: 34547847
Karki D, Nagila A, Dhakal N, Chhetri S. Prevalence of peripheral neuropathy in diabetes mellitus and its association with therapy, ethnicity and duration of diabetes mellitus. Asian Journal of Medical Science. 2019;10(1):72-6. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/341736658
Boulton AJM, Armstrong DG, Albert SF, Frykberg RG, Hellman R, Kirkman MS, et al. Comprehensive Foot Examination and Risk Assessment: a report of the task force of the foot care interest group of the American Diabetes Association, with endorsement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists. 2008;31(8):1679-85. PMID: 18663232 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2337/dc08-9021
Jordan DN, Jordan JL. Foot self-care practices among Filipino American women with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Ther. 2011;2(1):1-8. PMID: 22127764 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-010-0016-2
Alexiadou K, Doupis J. Management of diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetes Ther. 2012;3(1):4. PMID: 22529027 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-012-0004-9
Moxey PW, Gogalniceanu P, Hinchliffe RJ, Loftus IM, Jones KJ, Thompson MM, et al. Lower extremity amputations--a review of global variability in incidence. Diabet Med. 2011;28(10):1144-53. PMID: 21388445 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-5491.2011.03279.x
Saber HJ, Daoud AS. Knowledge and practice about the foot care and the prevalence of the neuropathy among a sample of type 2 diabetic patients in Erbil, Iraq. J Family Med Prim Care. 2018;7(5):967-74. PMID: 30598942 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_163_18
Sharma S.K. Nursing Research and Statistics. 2nd Ed. Elsevier: India; 2019
Lincoln NB, Jeffcoate WJ, Ince P, Smith M, Radford KA. Validation of a new measure of protective foot care behaviour: the Nottingham Assessment of Functional Footcare (NAFF). Practical Diabetes International. 2007;24(4):207-11. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pdi.1099
Brown MB, Feldman EL, Funnel MM, Greene DA, Stevens MJ. Michigan Neuropathy Screening Instrument (MNSI) [Internet]. University of Michigan; 1994. [cited 2021 Sep 8]. Available from: https://eprovide.mapi-trust.org/instruments/michigan-neuropathy-screening-instrument
George H, Rakesh P, Krishna M, Abraham VJ, George K, Prasad JH. Foot care knowledge and practices and the prevalence of peripheral neuropathy among people with diabetes attending a secondary care rural hospital in southern India. J Family Med Prim Care. 2013;2(1):27-32. PMID: 24479039 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/2249-4863.109938
Khawaja N, Abu-Shennar J, Saleh M, Dahbour SS, Khader YS, Ajlouni KM. The prevalence and risk factors of peripheral neuropathy among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus ; the case of Jordan. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2018;10(0):8. PMID: 29483946 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13098-018-0309-6
Shiferaw WS, Akalu TY, Work Y, Aynalem YA. Prevalence of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Endocrine Disorders. 2020;20(0):49. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12902-020-0534-5
Amour AA, Chamba N, Kayandabila J, Lyaruu IA, Marieke D, Shao ER, et al. Prevalence, Patterns, and Factors Associated with Peripheral Neuropathies among Diabetic Patients at Tertiary Hospital in the Kilimanjaro Region: Descriptive Cross-Sectional Study from North-Eastern Tanzania. Int J Endocrinol. 2019;2019(0):5404781 PMID: 31275374 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5404781
Begum S, Venkatesan M, Ganapathy K. Foot care practices, its barriers and risk for peripheral neuropathy among diabetic patients attending medical college in rural Puducherry. International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health. 2019;6(1):203-7. DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2394-6040.ijcmph20185243
Sun J, Wang Y, Zhang X, Zhu S, He H. Prevalence of peripheral neuropathy in patients with diabetes : A systematic review and meta-analysis. Prim Care Diabetes. 2020;14(5):435-44. PMID: 31917119 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcd.2019.12.005
Kisozi T, Mutebi E, Kisekka M, Lhatoo S, Sajatovic M, Kaddumukasa M. Prevalence, severity and factors associated with peripheral neuropathy among newly diagnosed diabetic patients attending Mulago hospital : a cross-sectional study. Afr Health Sci. 2017;17(2):463-73. PMID: 29062342 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4314/ahs.v17i2.21
Bansal D, Gudala K, Muthyala H, Esam HP, Nayakallu R, Bhansali A. Prevalence and risk factors of development of peripheral diabetic neuropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus in a tertiary care setting. J Diabetes Investig. 2014;5(6):714-21. PMID: 25422773 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jdi.12223
Katulanda P, Ranasinghe P, Jayawardena R, Constantine GR, Sheriff MR, Matthews DR. The prevalence, patterns and predictors of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in a developing country. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2012;4(1):1-8. PMID: 22642973 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1758-5996-4-21
Jatooi NA, Alsulaiman ASA, Alromaih NJ, Abdullah Albahrani B, Alkhattaf IM, Alyami F, et al. Prevalence of diabetic peripheral neuropathy among type II diabetic patients in King Fahd University Hospital, Khobar, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Hosp Pract (1995). 2021;49(2):63-70. PMID: 33216654 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/21548331.2020.1853995
Ugoya SO, Owolabi MO, Ugoya TA, Puepet FH, Echejoh GO, Ogunniyi A. The association between body mass index and diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Hungarian Medical Journal. 2008;2(1):63-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1556/hmj.2.2008.1.7
Shrestha TM, Aacharya RP, Shrestha R, KC M. Foot Care Knowledge and Practice among Diabetic Patients Attending General Outpatient Clinic in Tribhuvan University Teaching Hospital. Open Journal of Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases. 2017;7(8):163-71. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4236/ojemd.2017.78015
Gholap MC, Mohite VR. To assess the knowledge and practice regarding foot care among diabetes patients at Krishna hospital, Karad. Indian Journal of Scientific Research.2013;4(2):69-75. Available from: https://www.indianjournals.com/ijor.aspx?target=ijor:ijsr1&volume=4&issue=2&article=012
Muhammad-Lutfi AR, Zaraihah MR, Anuar-Ramdhan IM. Knowledge and Practice of Diabetic Foot Care in an In- Patient Setting at a Tertiary Medical Center. Malays Orthop J. 2014;8(3):22-6. PMID: 26401231 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5704/moj.1411.005
Sutariya PK, Kharadi A. Knowledge and practice of foot care among the patients of diabetic foot:a hospital based cross-sectional study. International Surgery Journal. 2016;3(4):1850-5. DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20163045
Abu-elenin MM, Elshoura AA, Alghazaly GM. Knowledge, Practice and Barriers of Foot Self-Care among Diabetic Patients at Tanta University Hospitals, Egypt. The Egyptian Journal of Community Medicine. 2018;36(4):94-102. DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.21608/ejcm.2018.23001
Al-Gaows FS, Al-Zahrani AM. Knowledge and Practice of Foot Care Among Diabetic Patients Attending Diabetic Care Center in Jeddah City. International Journal of Medical Reviews and Case Reports. 2019;3(11):664-70. DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5455/IJMRCR.Knowledge-and-Practice-diabetes
Chatterjee S, Basu M, Bandyopadhyay K, De A, Dutta S. Knowledge and practice of foot care amongst diabetic patients attending a tertiary care hospital of Kolkata, India. Journal of Preventive Medicine and Holistic Health. 2017;3(1):15-21. Available from: https://www.jpmhh.org/article-details/4419
Pavithra H, Akshaya KM, Nirgude AS, Balakrishna AG. Factors associated with awareness and practice about foot care among patients admitted with diabetes mellitus: A cross sectional research from a medical college hospital of southern India. Nepal J Epidemiol. 2020;10(3):897-904. PMID: 33042593 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3126/nje.v10i3.29213
Seid A, Tsige Y. Knowledge, Practice, and Barriers of Foot Care among Diabetic Patients AttendingFelegeHiwot Referral Hospital, Bahir Dar, Northwest Ethiopia. 2015;2015(0):934623. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/934623
Pourkazemi A, Ghanbari A, Khojamli M, Balo H, Hemmati H, Jafaryparvar Z, et al. Diabetic foot care: knowledge and practice. BMC EndocrDisord. 2020;20(1):40. PMID: 32192488 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12902-020-0512-y
Magbanua E, Lim-Alba R. Knowledge and Practice of Diabetic Foot Care in Patients with Diabetes at Chinese General Hospital and Medical Center. J ASEAN Fed Endocr Soc. 2017;32(2):123-31. PMID: 33442095 DOI: https://doi.org/10.15605/jafes.032.02.05
Published
Issue
Section
License
- The Journal of Lumbini Medical College (JLMC) publishes open access articles under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) License which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- JLMC requires an exclusive licence to publish the article first in its journal in print and online.
- The corresponding author should read and agree to the following statement before submission of the manuscript for publication,
- License agreement
- In submitting an article to Journal of Lumbini Medical College (JLMC) I certify that:
- I am authorized by my co-authors to enter into these arrangements.
- I warrant, on behalf of myself and my co-authors, that:
- the article is original, has not been formally published in any other peer-reviewed journal, is not under consideration by any other journal and does not infringe any existing copyright or any other third party rights;
- I am/we are the sole author(s) of the article and have full authority to enter into this agreement and in granting rights to JLMC are not in breach of any other obligation;
- the article contains nothing that is unlawful, libellous, or which would, if published, constitute a breach of contract or of confidence or of commitment given to secrecy;
- I/we have taken due care to ensure the integrity of the article. To my/our - and currently accepted scientific - knowledge all statements contained in it purporting to be facts are true and any formula or instruction contained in the article will not, if followed accurately, cause any injury, illness or damage to the user.
- I, and all co-authors, agree that the article, if editorially accepted for publication, shall be licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0. If the law requires that the article be published in the public domain, I/we will notify JLMC at the time of submission, and in such cases the article shall be released under the Creative Commons 1.0 Public Domain Dedication waiver. For the avoidance of doubt it is stated that sections 1 and 2 of this license agreement shall apply and prevail regardless of whether the article is published under Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 or the Creative Commons 1.0 Public Domain Dedication waiver.
- I, and all co-authors, agree that, if the article is editorially accepted for publication in JLMC, data included in the article shall be made available under the Creative Commons 1.0 Public Domain Dedication waiver, unless otherwise stated. For the avoidance of doubt it is stated that sections 1, 2, and 3 of this license agreement shall apply and prevail.
Please visit Creative Commons web page for details of the terms.












